
Getting Started: The 8 ICF Core Competencies
The ICF core competencies are crucial skills that every coach should possess. To make it easier to remember them, let’s use a clustering technique. Imagine a staircase with four major steps, each containing core competencies.
The first step is the foundation, including your ethical practice and your coaching mindset, which sets your baseline for effective coaching.
The next three steps are co-creating the relationship, communicating effectively, and cultivating learning and growth.
Each step contains one or more of the eight ICF core competencies: demonstrate ethical practice, embody a coaching mindset, establish and maintain agreements, cultivate trust and safety, maintain a presence, listen actively, evoke awareness, and facilitate client growth.

By visualizing this staircase, you can easily recall and understand the 8 ICF core competencies of coaching.
If you were used to the previous version of the ICF core competencies, this comparison table might help you to understand where the coaching competencies you had previously learned now belong:
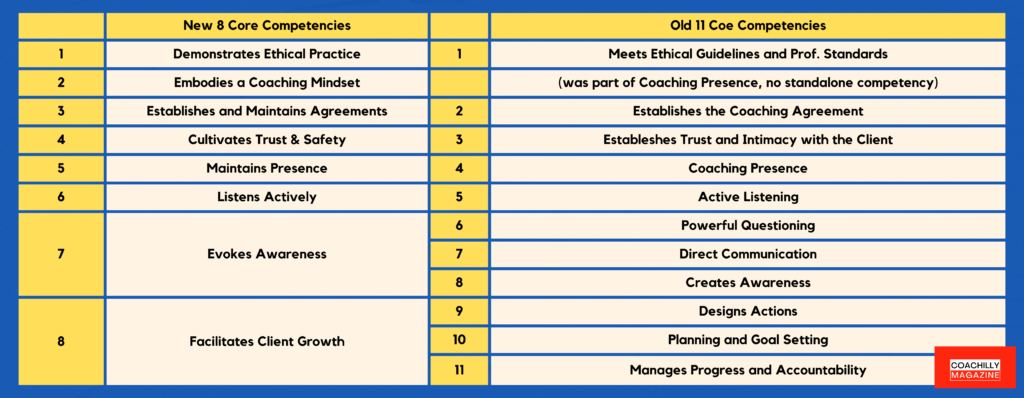
1. Ethical Guidelines and Professional Standards
The first of the ICF Core Competencies is Demonstrate Ethical Practice. This competency emphasizes the importance of conducting coaching sessions with the highest level of integrity, honesty, and transparency.
Ethical practice addresses key concerns such as respecting confidentiality, maintaining professional boundaries, and ensuring the well-being of clients. By upholding ethical standards, coaches establish trust with their clients and create a safe space for open and honest dialogue.
Why It Matters
This competency matters because it builds credibility and establishes a foundation of trust, allowing coaches to effectively support their clients in achieving their goals. Embodying ethical practice also helps coaches maintain their professional reputation and adhere to industry standards.
Examples Of Ethical Dilemmas And How To Handle Them
Ethical dilemmas can arise in the coaching profession, such as conflicts of interest or confidentiality concerns.
For example, a coach may face a situation where they have a personal relationship with a client outside of coaching. In such cases, coaches need to maintain professional boundaries and avoid any potential conflicts, respecting the Code of Ethics.
Coaches should prioritize confidentiality with client information and respect their privacy, ensuring that information shared during coaching sessions remains confidential.
By adhering to the ICF Core Competency of Demonstrate Ethical Practice, coaches can navigate these ethical dilemmas and build trusting relationships with their clients.
2. Coaching Mindset
A coaching mindset is deeply influenced by the quality and nature of coaching interactions, referring to the attitude and approach a coach takes in these engagements with clients.
A coach with a proper mindset is not fixed on a specific outcome or attached to their expertise; rather, they are focused on facilitating the client’s exploration and self-discovery. This competency underlines the importance of continual self-development, awareness, reflective practice, and maintaining a client-centered coaching approach.
Why It Matters
A coaching mindset is essential as it underpins the coaching relationship by fostering trust, ensuring openness to the client’s views, and allowing a real exploratory process for personal insights. It equips coaches to be flexible to shifting client needs and to establish a safe, supportive environment that encourages open exploration of both challenges and opportunities. This mindset is foundational for transformative coaching experiences.
Strategies To Develop A Coaching Mindset
- Reflective Practice: Consider what went well and what could be improved, focusing on your presence, not just your actions.
- Cultivate Curiosity: Be genuinely interested in learning about your client’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences without making assumptions.
- Self-Development: Engage in ongoing learning and development to enhance your coaching skills and personal growth.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly ask for feedback from your clients and peers to gain different perspectives on your coaching style and effectiveness. We also provide resources at the end of this guide to get specific feedback for your application of the ICF Core Competencies.
- Mindfulness and Presence: Develop a mindfulness practice to help you stay present and attentive during coaching sessions.
Examples Of Adopting A Coaching Mindset In Different Situations
In a team development session, guided by the ICF Team Coaching Competencies, a coach might observe a conflict between team members and instead of proposing a solution, would ask reflective questions like, “What do each of you feel is contributing to this challenge?” and “How might understanding each other’s viewpoints lead to a resolution?”
This approach applies the coaching mindset by encouraging self-reflection and mutual understanding, rather than imposing solutions, thereby empowering the team members to collaboratively find a resolution that aligns with their collective goals. The coach’s role is to facilitate awareness and encourage the team to actively engage in their growth process.
3. Establish and Maintain Agreements
The ICF competency of ‘Establish and Maintain Agreements’ refers to the coach’s ability to understand and effectively set the parameters of the coaching relationship, including the identification and agreement on specific coaching objectives.
This process involves establishing clarity regarding the coaching process, defining the roles and responsibilities of both the coach and the client, and setting the objectives and terms of the coaching engagement.
Why It Matters
This competency is critical because it ensures that both coach and client understand the purpose and direction of their work together, fostering an environment of mutual respect.
Clear agreements provide structure and define the scope of the coaching, leading to more focused and purposeful sessions.
It also ensures accountability and professionalism within the coaching relationship, contributing to an atmosphere of respect for each other’s roles and boundaries.
7 Steps To Effectively Establish A Coaching Agreement
- Clarify the Purpose: Begin by understanding and agreeing on the purpose of the coaching relationship.
- Define the Scope: Clearly define what is included in the coaching sessions and what may be beyond the scope.
- Set the Objectives: Collaboratively establish the goals and objectives of the coaching engagement.
- Outline the Process: Describe the coaching process, including session frequency, duration, and methodologies used.
- Discuss Logistics: Agree on the logistics, such as meeting times, locations (physical or virtual), payment terms, and cancellation policies.
- Ensure Understanding: Make sure both parties fully understand and agree to the terms before proceeding.
- Revise as Needed: As the coaching progresses, be prepared to revisit and revise the agreement, ensuring that it continues to meet the client’s needs and the objectives of the coaching engagement. This step often reaches agreement on adaptations that may be necessary as goals evolve or circumstances change.
4. Cultivate Trust and Safety
This competency requires the coach to adeptly cultivate an environment characterized by trust, openness, and psychological security, especially when navigating strong emotions in the coaching dynamic.
It involves creating a space where clients feel comfortable to explore their thoughts, and feelings, and engage in authentic self-expression without fear of judgment.
Facilitating client self-expression is vital for deepening the coaching relationship, as it allows clients to freely share their experiences, perspectives, and aspirations.
Why It Matters
When clients feel safe and supported, they are more likely to be honest, open, and receptive to the coaching process, providing coaches with vital client insights. Trust allows for deeper exploration and facilitates meaningful breakthroughs based on these insights.
3 Practical Tips For Building A Strong Coaching Relationship
- Active Listening: Active listening is a fundamental skill in coaching that involves fully concentrating on what the client is saying, understanding the message, and responding thoughtfully.
- Empathy and Compassion: Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings of another person, while compassion involves showing genuine concern and support. By acknowledging and validating the client’s emotions and experiences, coaches create a safe space where clients feel understood.
- Establishing Boundaries: Establishing and maintaining professional boundaries is crucial for creating a sense of safety and structure within the coaching relationship. Coaches need to clearly define boundaries regarding topics of discussion, the coaching process, and the coach-client relationship.
Real-Life Examples Of Successful Co-Creation In Coaching
Client-Centered Goal Setting:
A coach works with a client who wants to advance their career but feels stuck. Instead of prescribing goals, the coach engages in a collaborative process with the client. Together, they explore the client’s aspirations, values, and strengths.
Through this exploration, they identify specific career goals that are meaningful and aligned with the client’s values and aspirations. By co-creating these goals, the client feels a sense of ownership and commitment, which enhances their motivation and dedication to achieving them.
Exploration of Values and Beliefs:
In another coaching session, a coach helps a client who is struggling with work-life balance. The coach and client engage in a collaborative exploration of the client’s values and beliefs surrounding work and life.
Through open dialogue and reflective questioning, they uncover underlying beliefs that are contributing to the client’s imbalance.
The coach supports the client in gaining clarity about their values and aligning them with their actions and decisions. By co-creating this understanding, the client feels empowered to make intentional choices that honor their values, leading to a greater sense of fulfillment and balance.
5. Maintain Presence
Maintaining presence involves the coach’s capacity to remain fully engaged, attentive, and focused during coaching conversations, ensuring impactful interactions with clients.
It encompasses being emotionally and mentally attuned to the client, actively listening, observing non-verbal cues, and authentically responding to their needs and concerns during these sessions.
The unique dynamics of each individual session demand the coach’s complete presence to effectively support the client’s exploration and future growth, ensuring that every session is maximized for the client’s benefit.
Why It Matters
When coaches are fully present, clients feel heard, valued, and supported, which enhances trust and rapport.
Coaching presence allows coaches to pick up on subtle cues and nuances in the client’s communication, facilitating better insight and understanding.
Tips For Enhancing Communication Skills In Coaching
| Cultivate Self-Awareness | Practice Reflective Inquiry |
| Utilize Silence | Show Genuine Interest |
| Validate and Affirm | Engage in Active Presence |
6. Listen Actively
Active listening is a cornerstone of effective coaching conversations, going beyond simply hearing what the client is saying to understand the underlying meaning and context.
It entails giving the client undivided attention, demonstrating empathy, and reflecting on what is being communicated to ensure clarity and understanding.
This part of the ICF core competencies emphasizes the importance of being fully present and attentive during coaching sessions to facilitate meaningful dialogue and exploration.
Why It Matters
By actively listening, coaches validate their clients’ experiences, fostering a sense of being heard and valued. This validation, in turn, nurtures trust and openness within the coaching relationship, creating a safe space for clients to explore their thoughts and feelings.
Strategies To Improve Active Listening As A Coach
- Practice Mindful Listening: Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing or focusing on the present moment, can help coaches stay present and attentive during coaching sessions.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Pay attention to non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice to gain deeper insight into the client’s emotions and intentions. Non-verbal cues often provide valuable information that complements verbal communication. If a client appears tense or fidgety during a discussion about a particular topic, it may indicate discomfort or anxiety. Acknowledge these non-verbal cues and explore the underlying emotions with sensitivity and empathy.
- Active Engagement: Demonstrate active engagement by nodding, maintaining eye contact, and providing verbal affirmations to show that you are listening and fully present. Active engagement encourages clients to continue sharing and fosters a sense of being heard and understood. During coaching sessions, actively engage with the client by nodding your head, making eye contact, and offering verbal affirmations such as “I understand” or “That makes sense.” This reassures the client that you are attentive and supportive.
7. Evoke Awareness
Coaches use various techniques to facilitate clients’ self-discovery and promote a deeper understanding of their beliefs, values, and goals, while also identifying and addressing potential barriers to their progress.
By asking thought-provoking questions, offering reflections, and providing feedback, coaches not only support clients in exploring new perspectives but also help them recognize and overcome the obstacles that may hinder their growth and transformation.
Why It Matters
Evoke Awareness is crucial in coaching because it empowers clients to identify and challenge limiting beliefs, explore new possibilities, and make conscious choices aligned with their values and aspirations.
The heightened awareness fosters self-confidence, resilience, and personal agency, enabling clients to navigate challenges and thrive in all aspects of their lives.
Asking Powerful Questions As A Coach
The best technique for asking powerful questions as a coach is the GROW model. GROW stands for Goal, Reality, Options, and Way Forward. This structured approach helps coaches guide clients through a process of self-exploration and problem-solving.
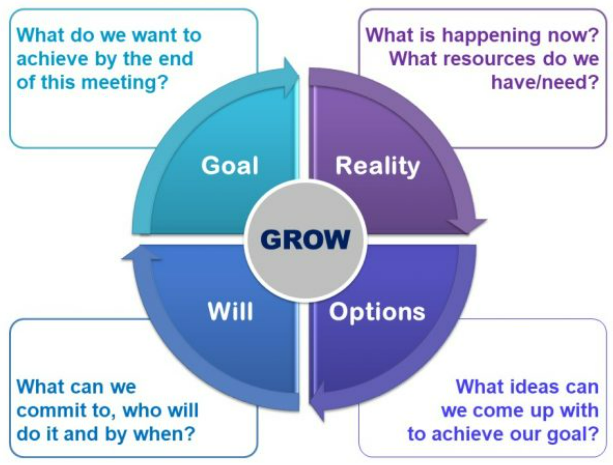
Image courtesy of Coachingcultureatwork.com
- Goal: Begin by clarifying the client’s desired outcome or goal for the coaching session. Encourage the client to articulate their aspirations, values, and priorities to establish a clear direction for exploration.
- Reality: Explore the client’s current reality by asking questions that encourage honest reflection and assessment, identifying factors contributing to or hindering client progress.
- Options: Generate a range of options and possibilities for achieving the client’s goal. Encourage powerful questioning techniques like creative thinking and brainstorming by asking open-ended questions that stimulate exploration and challenge assumptions.
- Way Forward: Support the client in developing a concrete action plan or strategy to move forward. Help the client identify specific steps, resources, and accountability measures to support their progress and sustain momentum toward their goal.
Guideline For Practicing Direct Communication In Coaching
Clarity and Precision
Clearly articulate your message using language that is easily understandable and devoid of ambiguity. Employ concrete examples and specific feedback to ensure clarity.
Issue-Centric Approach
Address the matter at hand, focusing on behavior or challenges rather than criticizing the individual. Utilize non-judgmental language and refrain from making assumptions about the client’s character.
Empowerment and Autonomy
Respect the client’s autonomy by presenting information and options impartially, without imposing personal biases.
Encourage clients to explore their values, preferences, and goals independently to foster a sense of empowerment and ownership. Implement methods of accountability to ensure that clients are actively engaged in the coaching process and committed to their goals.
Empathetic Engagement
Practice empathetic communication by demonstrating understanding and compassion toward the client’s experiences and emotions. Build trust and rapport by validating their feelings and creating a supportive environment for open dialogue.
8. Facilitate Client Growth
Facilitating client growth is a pivotal core competency within the International Coach Federation (ICF) framework, underscoring the fundamental goal of coaching: to guide and support clients throughout their coaching journey toward realizing their full potential, both personally and professionally.
This entails a focused approach to understanding and aligning with client goals, fostering deeper learning about themselves and their possibilities, and defining clear action steps that the client can take towards achieving these goals.
By collaboratively identifying these goals, delving into deeper learning for meaningful insights, and developing an effective coaching plan, coaches ensure that the insights and discoveries made during the coaching sessions translate into tangible progress and real-world outcomes.
Why It Matters
- Empowers Clients: This skill empowers coaching clients to own their development, guiding them to discover their desires, strengths, and challenges, fostering self-reliance and confidence.
- Promotes Self-Discovery: It motivates clients towards self-exploration, revealing their core values, beliefs, and motivations, paving the way for more meaningful, sustainable changes aligned with their identity.
- Encourages Action and Accountability: Coaches assist clients in turning insights into client actions, creating momentum for goal achievement and instilling accountability for their progress.
- Facilitates Lasting Change: By emphasizing growth, this approach supports enduring transformations as clients apply newly developed skills and strategies across life areas.
- Builds Resilience: It strengthens clients’ resilience, helping them to view setbacks as opportunities for growth, thus improving their adaptability and ability to overcome adversity.
- Enhances Life Satisfaction: Enhancing client growth boosts life satisfaction by helping clients reach significant personal and professional milestones, positively affecting their well-being, relationships, and performance.
Best Practices Example Of Facilitating Client Growth
In a scenario where a client, Alex, aims to transition to a leadership role, the coach employs key practices to facilitate Alex’s growth effectively.
Building Trust and Goal Setting
Initially, the coach establishes a trusting environment, enabling Alex to openly share ambitions and concerns. Together, they define a clear goal: to become an effective leader within six months, outlining specific leadership qualities Alex aspires to develop.
Encouraging Reflection and Action Planning
Through insightful questioning, the coach prompts Alex to reflect on personal strengths, areas for improvement, and any limiting beliefs. Identifying a belief that technical experts don’t make good leaders, Alex is guided to challenge this notion. They collaboratively create an action plan focusing on leading a team project, seeking a mentor coach, and attending a leadership workshop, setting measurable milestones.
Fostering Accountability and Resilience
Regular check-ins maintain Alex’s motivation and adapt the plan as needed, promoting accountability. When Alex faces a setback, the coach encourages viewing it as a growth opportunity, enhancing Alex’s resilience and adaptability.
Reinforcing Growth and Celebrating Progress
Throughout, the coach emphasizes a growth mindset, celebrating Alex’s achievements and learnings. This reflection boosts Alex’s confidence and highlights the journey’s value in achieving leadership aspirations.
This streamlined approach illustrates how trust-building, goal clarity, resilience-building, and progress celebration are central to facilitating client growth.
A Quick Recap
The ICF Core Competencies & Their Importance
The ICF Core Competencies represent the gold standards of coaching, offering a comprehensive framework that guides coaches in facilitating effective, ethical, and transformative coaching engagements.
These coaching competencies ensure that coaches are equipped with the essential skills, attitudes, and knowledge to support their clients’ growth and development, adhering to the highest professional and ethical standards.
By mastering the ICF core competencies, coaches commit to excellence in their practice, contributing to the overall credibility and effectiveness of the coaching profession.
Applying ICF Core Competencies in Your Coaching Practice
Practicing these competencies, receiving feedback, and engaging in continuous learning are essential steps in a coach’s professional development journey. Here are some excellent resources and platforms where you can apply the ICF Core Competencies, practice your skills, and receive valuable feedback from your peers:
- ReciproCoach
- ReciproCoach offers a unique model that allows coaches to practice coaching with each other, applying the ICF Core Competencies in real scenarios. It’s an excellent opportunity for coaches to receive constructive feedback from peers who are also familiar with the competencies, facilitating mutual growth and learning.
- The Coaching Supervision Academy
- The Coaching Supervision Academy provides coaching supervision services where coaches can reflect on their practice, receive feedback, and gain deeper insights into their coaching style and methodology. Supervision sessions are a great place to explore the application of ICF Core Competencies in-depth, with guidance from experienced supervisors committed to upholding the gold standards of coaching.
- International Coach Federation (ICF) Communities of Practice
- ICF’s Communities of Practice (CoP) offers a collaborative environment for coaches to discuss specific coaching themes, challenges, and best practices. Participating in these communities allows coaches to apply the ICF Core Competencies in discussions, receive feedback from a diverse group of coaches, and stay updated on the latest trends and developments in coaching.
- CoachU Core Essentials Program
- CoachU’s Core Essentials Program is designed to provide foundational coach training aligned with the ICF Core Competencies. This program offers both theoretical knowledge and practical application opportunities through coaching practice sessions. Participants can receive feedback on their coaching from experienced trainers and peers, making it an ideal place to hone one’s coaching skills in alignment with ICF standards.
These platforms and resources not only provide opportunities for applying and practicing the ICF Core Competencies but also offer a supportive environment for receiving feedback and engaging in continuous professional development.
By taking advantage of these resources, coaches can ensure they remain at the forefront of the coaching profession, effectively supporting their clients’ growth and achieving their professional milestones.
